Causes Of Weakness In The Legs In Elderly

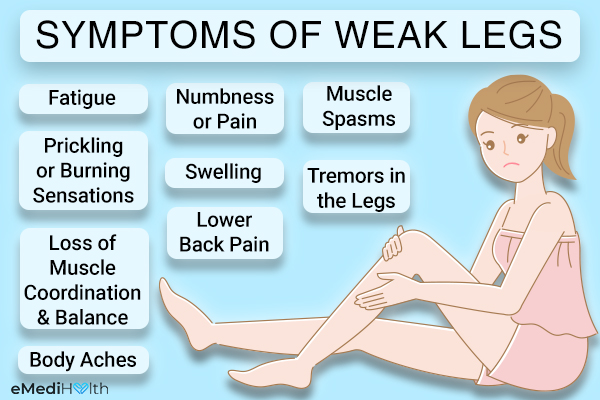
While those are among the most common causes of sudden leg weakness in the elderly sudden weakness in the legs can also be caused by a stroke and a laundry list of less common conditions like Guillain-Barre syndrome Multiple sclerosis peripheral neuropathy Parkinsons ALS spinal tumors and others.
Causes of weakness in the legs in elderly. Poor dietary intake can result in weak leg muscles. While those are among the most common causes of sudden leg weakness in the elderly sudden weakness in the legs can also be caused by a stroke and a laundry list of less common conditions like Guillain-Barre syndrome Multiple sclerosis peripheral neuropathy Parkinsons ALS spinal tumors and others. Multiple sclerosis also causes weakness in the legs and the Multiple Sclerosis Society explains that vitamin D deficiency may be a contributing factor.
The changes in lean muscle tissue often begin in the 20s for men and 40s for women. Immobility Immobility and sedentary lifestyles play a significant role in the onset and progression of sarcopenia. Some of the most common causes include depression issues with blood circulation impaired breathing for example chronic obstructive pulmonary disease hormone imbalances like hypothyroidism.
Leg weakness in older people can have a myriad of other causes. R worse and calf mus hurts. An 85-year-old woman presented to hospital in March 2012 for evaluation of left leg weakness.
Failing to exercise muscles increases weakness in them and makes muscle loss occur more quickly. Causes of leg weakness in the elderly. What can cause bi lateral generalised leg weakness with difficulty to step up without grabbing pain in top of leg.
8 Main Causes of Sudden Leg Weakness in Seniors. Failure to pace describes a situation in which pacing should occur but the pacemaker does not fire. What causes weakness in legs in the elderly.
For example some housebound elderly develop muscle weakness due to extreme vitamin D deficiency. Physically inactive people tend to lose muscle mass by 3-5. When the disc shifts or loses its gelatinous contents the surrounding vertebrae cause pressure on spinal nerves which may lead to leg pain and weakness.